If you are unfamiliar with the term REST API and you need further explanation - in a nutshell, the term represents any web services using the REST architecture that involves reading a designated Web page that contains an XML\JSON file.
The media that goes processed through the REST (Representational State Transfer) thus utilizing the HTTP Protocol is also cost-effective in terms of bandwidth that makes it a better fit for the Internet traffic and simplicity of use.
In most recent news, the design of the API that supports the REST interfaces has found to be growing progressively. The integration and development of the application architecture is subtly changing, and the world has come to a point where APIs are not a privilege anymore, but a common need.

Now, the REST today is bound to run over the HTTP protocol and has the following constraints or some may call it features:
- It is able to decouple the link between consumers and producers
- It is known as a stateless existence
- It is able to introduce the cache effect helping our search and digital data storage
- It introduces a fully layered system
- It establishes itself as a uniform interface
- The REST API testing is very easing because it is based on the HTTP protocol.
Whether it is present in social networks, mobile apps, mashup tools or complicated business processes, the REST APIs are now present everywhere - simply encompassing the interaction between the web services and clients in a better and more engaging way. And while the style of SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol), a competitor of the REST framework has been found to be a little bit of old-fashioned and made for the classic middle-ware design - as said by programmers - the REST API interfaces have made the designing process a lot more easier - starting from the very general to the very specific, which is a revolutionary step ahead in technology.
In practice, the REST interface comes up when the control is gone and there are many open-ended use cases, collaborations with other users and the need for being tolerant. In other words, REST is perfectly well made for the cloud, mobile and other innovative and fast access to information areas which are considered to be the future of the Web. As the world has shown its interest for mobile and cloud, the REST interface progressively grew, making the interface fit on the consistent infrastructure capabilities of nowadays, limited communications and cases involving a large number of counter parties.
Popularity with numbers:
Here are some numbers over the years to demonstrate the raise of REST APIs popularity based on in the ProgrammableWeb’s directory of more than 14,000 web APIs.
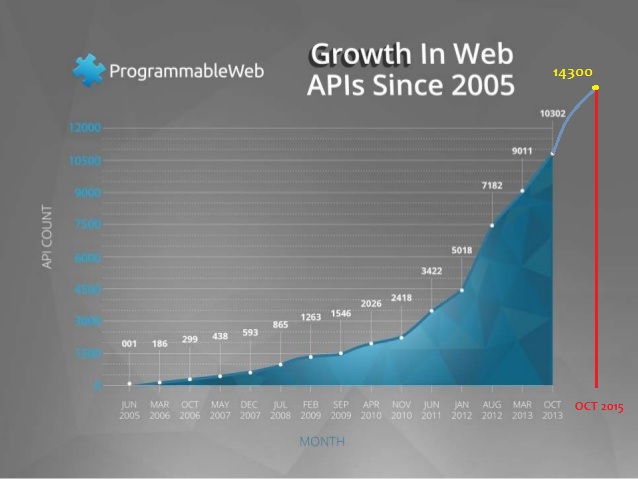
Yes, I added the last "number" myself (I am not the perfect designer out there so bare with me):
Interest over time for REST API versus SOAP API:
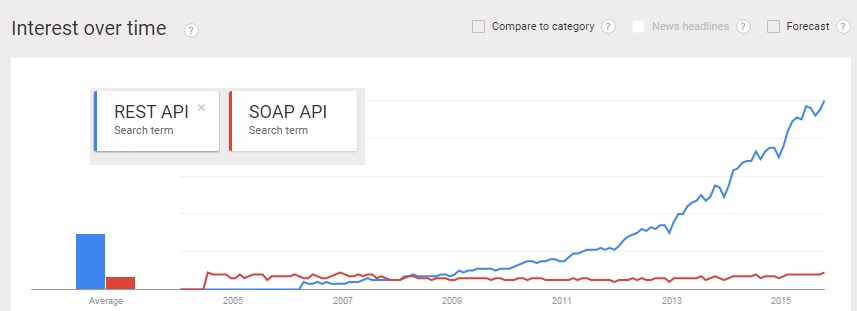
Source - Google Trends
It seems that REST API popularity is only increasing and REST is the dominant API style by far while interest in SOAP is declining.
We can also see that in one of the largest independent and publicly available directories for APIs (ProgrammableWeb), the share of Internet APIs by technology in March 2014 is:
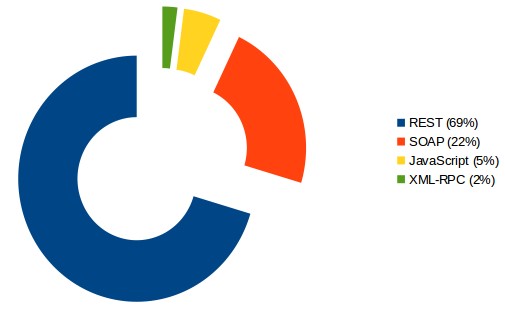 REST (69%), SOAP (18%), JavaScript (5%), and XML-RPC (2%).
REST (69%), SOAP (18%), JavaScript (5%), and XML-RPC (2%).
We can see that SOAP is being used less and less while REST is becoming more and more popular.
So what is the prospected future?
- REST APIs ‒ approaching.
- Semantic REST APIs ‒ future.
What or Who drives the popularity of REST APIs?
In the past:
- 2006: API pioneers eBay, Amazon and Google Maps were among the first to offer popular Web APIs.
- 2007: The mobile revolution kicked off by smart phones.
- 2013: Mobile and infotainment platforms diversity (Jolla, BB10, Tizen, Ubuntu, WP, FF OS, Android...).
In the future:
- 2015+: Babylonic language diversity (Only some newer ones: Rust, Go, Dart).
- 2016+: Internet of things (vehicles, household appliances, ...every power plug).
- 15B connected devices in 2015, 40B connected devices in 2020.
I think that it is obvious that the future belongs to REST APIs.